Background:
The modern concept of ESG, which we’re so familiar with today, took shape in the mid-2000s. However, the principles behind ESG are decades, maybe even centuries, old. Throughout the 20th century, we have seen plenty of campaigns pressuring companies into fairer, more sustainable business practices. Examples include efforts to stop the exploitation of workers, the funding of wars or oppressive regimes like apartheid, and the introduction of corporate governance codes – legal “rulebooks” telling companies how to manage themselves. Events like these demonstrated that governments, investors and consumers recognized the power of corporate entities to shape the world around them. Over time, this power came under more and more scrutiny.
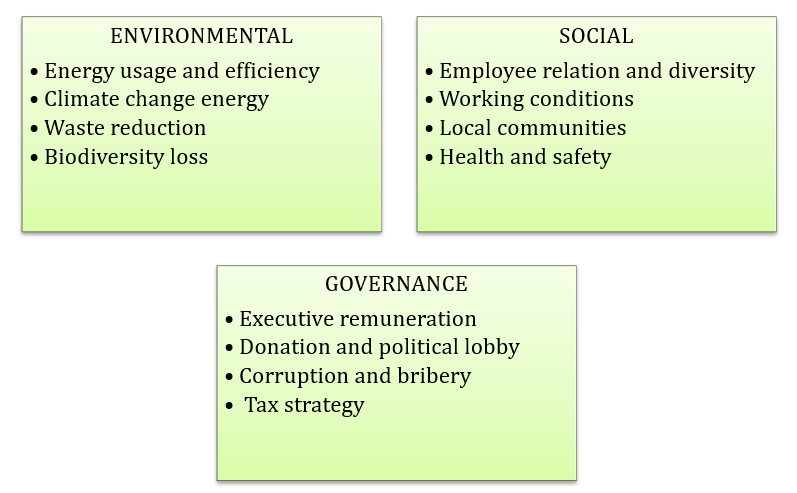
What is ESG?
ESG stands for Environmental, Social, and Governance. It is a set of considerations that can be used in investing and a framework used to assess an organization’s business practices and sustainability efforts.
- The environmental pillar refers to an organization’s environmental impact and risk management
- The social pillar refers to the organization’s impact on society
- The governance pillar refers to the organization’s management and decision-making processes.
How does ESG impact the function of audit?
ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting standards have an impact on the function of audit.
- The ESG standards that an auditor’s organization has selected provide the necessary requirements to further identify the controls that are in place to ensure proper reporting and to test and verify that they are designed and operating as expected.
- The move towards enhanced reporting, particularly in areas that require forecasting into the future, raises the risk of directors and auditors being judged.
- An ESG audit is a process that evaluates the environmental and social risks of a company’s products or services. The goal of this audit is to identify any potential risks so they can be addressed before they occur.
- Each ESG audit provides insight into the company’s approach towards these issues. Conducting an ESG audit also helps businesses look at their supply-chain risks, risk management capabilities, and transparency with stakeholders
- The growing importance of ESG information has led to the need for third-party assurance, which enhances the reliability of ESG information
and builds confidence among stakeholders. Auditors conduct attestation engagements to provide assurance that ESG information is presented in accordance with the relevant reporting framework
Some common ESG risks that auditors should be aware of
- Climate change and environmental risks: These risks can impact a company’s reputation, financial performance, and compliance with regulations.
- Human capital management: Risks related to employee relations, workplace culture, and talent management can affect a company’s productivity, retention, and overall performance.
- Supply chain management: Risks in the supply chain, such as labor standards, health and safety, and environmental practices, can impact a company’s reputation and supply chain stability
- Health and safety: Companies need to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations and manage risks related to workplace accidents and illnesses.
- Labor standards: Auditors should be aware of risks related to wage gaps, working hours, and other labor practices that can impact a company’s reputation and compliance with regulations.
- Equality, diversity, and inclusion: Risks in these areas can lead to reputational damage, legal issues, and financial penalties.
- Shareholder rights and engagement: Risks related to shareholder rights, communication, and engagement can impact a company’s reputation and compliance with regulations.
- Board structure and diversity: Risks related to board diversity, succession planning, and governance can impact a company’s strategic decision-making and reputation.
- Corruption prevention: Auditors should be aware of risks related to corruption, bribery, and anti-competitive behavior that can impact a company’s reputation and compliance with regulations.
- Grievance procedures and systems: Risks related to grievance procedures and systems can impact a company’s reputation and compliance with regulations
How can auditors identify ESG risks in their clients’ operations
- Auditors can identify ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) risks in their clients’ operations by conducting a thorough assessment to identify and categorize pertinent ESG risks to the organization’s industry and operations, including ESG issues, climate change, and supply chain risks.
- Auditors can use their knowledge of the industry to ask questions about whether management has done a proper risk assessment that takes into account ESG factors, whether the assessment is complete, and if any supplementation of the assessment is needed.
- Auditors can also review the company’s sustainability reports and ESG information to ensure that they are consistent with the financial statements and that the risks are properly reflected in the accounts
- Additionally, auditors can assess the effectiveness of ESG-related controls and activities to help companies identify gaps, assess risks, and develop a recommended plan of action.
Benefits of ESG reporting
- ESG reporting enables companies to communicate key ESG risks and opportunities and how these issues are managed, organize business
dependencies and impacts on the environment and society, and communicate their resiliency to shifts in the environment and society
- ESG audits provide a structured approach to assess an organization’s performance and adherence to ESG principles, enhancing transparency, accountability, and sustainability. By conducting effective ESG audits, organizations can identify areas for improvement, mitigate risks, and enhance their reputation among stakeholders.
- ESG audits can verify the accuracy of the ESG-related data that a company discloses to its stakeholders and regulatory bodies, ensuring data accuracy and reliability
- Integrating ESG in the annual audit plan can help businesses ensure reliable, transparent ESG information that meets the needs of investors, customers, and employees
Conclusion:
The impact of ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) on the function of audit is significant. ESG considerations have become central to business practices, and audit and assurance services play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy, reliability, and accountability of ESG reporting. Auditors must consider whether ESG risks are properly reflected in the accounts to provide a true and fair view of the financial position of the company. They also play a crucial role in independently verifying and validating reported ESG information, enhancing the reliability of ESG reports and bolstering stakeholder confidence in the data. The rise of ESG accounting has made ESG information increasingly vital, resulting in significant opportunities for auditors. Therefore, ESG has a substantial impact on the function of audit, requiring auditors to adapt to the evolving landscape of ESG reporting and assurance.
Authors:
Umesh Vishwakarma
Manager | Email: umesh.vishwakarma@masd.co.in | LinkedIn
Suyash Pansare
Associate Consultant | Email: suyash.pansare@masd.co.in

